Name of the medicinal product
Sustanon 250, 250mg/ml solution for injection
Qualitative and quantitative composition

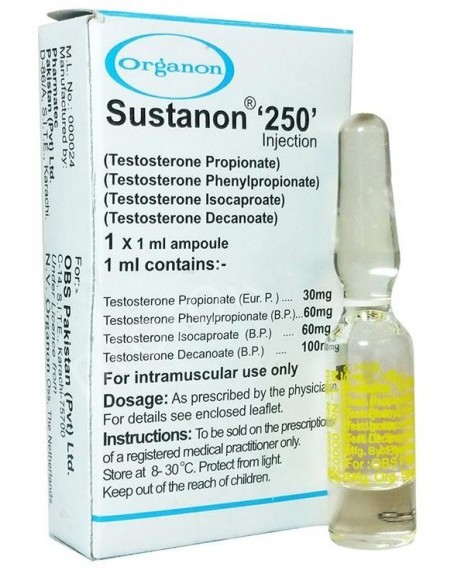
Sustanon 250 is a solution in oil. Each ampoule contains 1 ml arachis oil containing the following active substances:
- 30 mg Testosterone propionate
- 60 mg Testosterone phenylpropionate
- 60 mg Testosterone isocaproate
- 100 mg Testosterone decanoate
All four components are esters of the natural hormone testosterone. The total amount of testosterone per ml is 176 mg.
Pharmaceutical form
Solution for injection
A clear, pale yellow solution
Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Testosterone replacement therapy for male hypogonadism, when testosterone deficiency has been confirmed by clinical features and biochemical tests.
Testosterone administration may also be used as supportive therapy for female-to-male transsexuals.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Posology
In general, the dose should be adjusted to the response of the individual patient.
Adults (incl. elderly):
Usually, one injection of 1ml per 3 weeks is adequate.
Paediatric population
Safety and efficacy have not been adequately determined in children and adolescents. Pre-pubertal children treated with Sustanon 250 should be treated with caution (see section 4.4).
Female-to-male transsexuals:
Different specialist centres have used doses varying from one injection of 1ml every two weeks to one injection of 1ml every four weeks.
Method of administration
Sustanon 250 should be administered by deep intramuscular injection.
4.3 Contraindications
- Pregnancy (see section 4.6).
- Known or suspected carcinoma of the prostate or breast (see section 4.4.).
- Breast-feeding.
- Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients listed in section 6.1, including arachis oil. Sustanon 250 is therefore contraindicated in patients allergic to peanuts or soya (see section 4.4).
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Medical examination:
Testosterone level should be monitored at baseline and at regular intervals during treatment. Clinicians should adjust the dosage individually to ensure maintenance of eugonadal testosterone levels.
Physicians should consider monitoring patients receiving Sustanon 250 before the start of treatment, at quarterly intervals for the first 12 months and yearly thereafter for the following parameters:
• Digital rectal examination (DRE) of the prostate and PSA to exclude benign prostate hyperplasia or a sub-clinical prostate cancer (see section 4.3),
• Haematocrit and haemoglobin to exclude polycythaemia.

In patients receiving long-term androgen therapy, the following laboratory parameters should also be monitored regularly: haemoglobin, and haematocrit, liver function tests and lipid profile.
Conditions that need supervision:
Patients, especially the elderly, with the following conditions should be monitored for:
• Tumours – Mammary carcinoma, hypernephroma, bronchial carcinoma and skeletal metastases. In these patients hypercalcaemia or hypercalciuria may develop spontaneously, also during androgen therapy. The latter can be indicative of a positive tumour response to the hormonal treatment. Nevertheless, the hypercalcaemia or hypercalciuria should first be treated appropriately and after restoration of normal calcium levels, hormone therapy can be resumed.
• Pre-existing conditions – In patients suffering from severe cardiac, hepatic or renal insufficiency or ischaemic heart disease, treatment with testosterone may cause severe complications characterised by oedema with or without congestive cardiac failure. In such cases treatment must be stopped immediately. Patients who experienced myocardial infarction, cardiac-, hepatic- or renal insufficiency, hypertension, epilepsy, or migraine should be monitored due to the risk of deterioration of or reoccurrence of disease. In such cases treatment must be stopped immediately.
Testosterone may cause a rise in blood pressure and Sustanon 250 should be used with caution in men with hypertension.
• Epilepsy or Migraine – (or a history of these conditions), since androgens may occasionally induce fluid and sodium retention.
• Diabetes mellitus – Androgens in general and Sustanon 250 can improve glucose tolerance in diabetic patients (see section 4.5).
• Anti-coagulant therapy – Androgens in general and Sustanon 250 can enhance the anti-coagulant action of coumarin-type agents (see also section 4.5).
• Sleep apnoea – Caution should be applied when treating men with sleep apnoea. There have been reports that testosterone can cause or exacerbate pre-existing sleep apnoea. However, there is a lack of evidence regarding the safety of testosterone in men with the condition. Good clinical judgment and caution should be employed in patients with risk factors such as adiposity or chronic lung diseases.
Adverse events:
If androgen-associated adverse reactions occur (see section 4.8), treatment with Sustanon 250 should be discontinued and, upon resolution of complaints, resumed with a lower dose.
Virilisation:
Patients should be informed about the potential occurrence of signs of virilisation. In particular, singers and women with speech professions should be informed about the risk of deepening of the voice. The voice changes may be irreversible.
If signs of virilisation develop, the risk/benefit ratio has to be newly assessed with the individual patient.
(Mis)use in sports:
Patients who participate in competitions governed by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) should consult the WADA-code before using this product as Sustanon 250 can interfere with anti-doping testing. The misuse of androgens to enhance ability in sports carries serious health risks and is to be discouraged.
Drug abuse and dependence:
Testosterone has been subject to abuse, typically at doses higher than recommended for the approved indication(s) and in combination with other anabolic androgenic steroids. Abuse of testosterone and other anabolic androgenic steroids can lead to serious adverse reactions including: cardiovascular (with fatal outcomes in some cases), hepatic and/or psychiatric events. Testosterone abuse may result in dependence and withdrawal symptoms upon significant dose reduction or abrupt discontinuation of use. The abuse of testosterone and other anabolic androgenic steroids carries serious health risks and is to be discouraged.
Excipients:
Sustanon 250 contains Arachis oil (peanut oil) and should not be taken / applied by patients known to be allergic to peanut. As there is a possible relationship between allergy to peanut and allergy to soya, patients with soya allergy should also avoid Sustanon 250 (see section 4.3).
Sustanon 250 contains 100 mg benzyl alcohol per ml solution and must not be given to premature babies or neonates. Benzyl alcohol may cause toxic reactions and anaphylactoid reactions in infants and children up to 3 years old.
Female-to-male transsexual supportive therapy:
Before initiating Sustanon 250 for female-to-male transsexuals, specialist assessment should be undertaken, including psychiatric assessment. A complete personal and medical history should be taken. During treatment, periodic check-ups are recommended of a frequency and nature adapted to the individual. The following should be monitored:
- signs of osteoporosis,
- changes in lipid profile.
In patients with a personal or family history of breast cancer and with a personal history of endometrial cancer, careful monitoring should be undertaken.
Subject to specialist advice, hysterectomy and bilateral oophorectomy should be considered after 18-24 months of testosterone treatment, to reduce the possible increased risk of endometrial and ovarian cancer.
Continued surveillance is required to detect osteoporosis in patients who have undergone oophorectomy, as testosterone may not fully reverse the decline in bone density in these patients.
Continued surveillance is required to detect endometrial and ovarian cancer in patients on long term treatment who have not proceeded to hysterectomy and bilateral oophorectomy.
Paediatric population
In pre-pubertal children statural growth and sexual development should be monitored since androgens in general and Sustanon 250 in high dosages may accelerate epiphyseal closure and sexual maturation.
Older People:
There is limited experience on the safety and efficacy of the use of Sustanon 250 in patients over 65 years of age. Currently, there is no consensus about age specific testosterone reference values. However, it should be taken into account that physiologically testosterone serum levels are lower with increasing age.
Clotting disorders:
Testosterone should be used with caution in patients with thrombophilia or risk factors for venous thromboembolism (VTE), as there have been post-marketing studies and reports of thrombotic events (e.g. deep-vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, ocular thrombosis) in these patients during testosterone therapy. In thrombophilic patients, VTE cases have been reported even under anticoagulation treatment, therefore continuing testosterone treatment after first thrombotic event should be carefully evaluated. In case of treatment continuation, further measures should be taken to minimise the individual VTE risk.
How the injections are given
This medicine should only be given by a doctor or a nurse.
The injections are given deeply into a muscle (e.g. the buttock, upper leg or upper arm).
The contents of each vial or ampoule are for one injection only.
If you have the impression that the effect of this medicine is too strong or too weak, talk to your doctor or nurse immediately.
How much to take

Standard treatment is usually one injection of Sustanon ‘250’ every 3 weeks.
Dosage should be adjusted by your doctor in response to individual requirements.
Use in children and adolescents:
The safety and efficacy of this medicine have not been adequat
ely determined in children and adolescents. Pre-pubertal children using this medicine will be monitored by your doctor.
If you are given too much (overdose)
These injections are given under medical supervision and it is very unlikely that you will be given too much.
If several doses are given at once it is not a medical emergency. However you should consult your doctor as side effects are dependent on dosage, dose interval and your individual sensitivity.
Your doctor or nurse will inject this medicine into you. If you have the impression that the effect of this medicine is too strong then please talk to your doctor or nurse immediately.
If you forgot to get your injection of Sustanon
Your doctor or nurse will inject this medicine into you. Should you miss a scheduled injection then please talk to your doctor or nurse as soon as possible. No double dose should be injected to make up for forgotten individual doses.
While you are using Sustanon
Keep all of your appointments so that your progress can be checked. Your doctor may do some blood tests at regular intervals to make sure the medicine is working and to prevent unwanted side effects.
As far as known, Sustanon has no adverse effects on alertness and concentration.